Omega-3. The Purest EPA-DHA Fish Oil in the World
 For many years, Life Extension members were provided with omega-3 fish oil of extraordinary stability and purity. Not content with these lofty standards, a new fish oil has just come to market that provides consumers with an even better omega-3 blend at no additional charge!
For many years, Life Extension members were provided with omega-3 fish oil of extraordinary stability and purity. Not content with these lofty standards, a new fish oil has just come to market that provides consumers with an even better omega-3 blend at no additional charge!
Omega-3 fatty acids from cold-water fish have received an enormous amount of favorable publicity. One reason is that there have been more scientific studies to document fish oil’s multiple health benefits than perhaps any other nutrient.
Fish oil is available in a wide range of purities and potencies. Life Extension’s previous Super Omega-3 met such exacting standards that it achieved the highest rating awarded by a respected independent organization called the International Fish Oil Society.
Based on the availability of high-quality fish oil, you might wonder why a company would go to the effort of patenting a process to make an even purer EPA-DHA extract. The answer is free market competitive pressure. Since several high-quality fish oil producers control most of the supplement arena, one company felt it had to make an even better fish oil if it were to keep its leading position in the marketplace.
When evaluating the safety and potency of fish oil, the following three areas are analyzed:
- Stability: Fish oil can easily turn rancid, so a measurement of oxidative byproducts is a critical step to ensure that the omega-3 fatty acids you ingest are fresh.
- Purity: Cold-water ocean fish are rich in EPA/DHA, but are often contaminated with pollutants like PCBs, mercury, and arsenic. The fish oil you swallow should go through the purification processes needed to reduce contaminant levels to safe ranges.
- EPA-DHA consistency: The primary active ingredients in fish are eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA). Assaying fish oil to make sure it meets label claims is important to ensuring you are ingesting the desired amounts of EPA/DHA.
In order to protect consumers against unsafe and ineffective products, the Council for Responsible Nutrition has proposed strict guidelines for fish oil products. The good news is that this new fish oil extract exceeds even these proposed upgraded pharmaceutical standards.
This new fish oil extract is produced using a patented extraction and purification process to increase stability, remove virtually all contaminants, and protect against oxidation and peroxidation of the delicate omega-3 fatty acids. This new fish oil meets such high standards that it is approved in the European Union for use as an active pharmaceutical ingredient.
How this new fish oil is made
 To obtain a fish oil this pure and stable, a patented method was developed to purify the oil with an intense two-step distillation process. By purifying the oil before the intense distillation process, the result is a cleaner oil that has shorter heat exposure and prevents thermal (heat) degradation of the EPA/DHA.
To obtain a fish oil this pure and stable, a patented method was developed to purify the oil with an intense two-step distillation process. By purifying the oil before the intense distillation process, the result is a cleaner oil that has shorter heat exposure and prevents thermal (heat) degradation of the EPA/DHA.
These patented Pure+™ distillation processes remove other impurities that lead to reflux, burping, and regurgitation in some people. This new fish oil extract also smells better by virtue of these processes. This improved fish oil extract may even be tolerable to people with very sensitive stomachs.
The laboratory making this new fish oil extract was the first facility in the world approved to make pharmaceutical fish oil drugs.
No price increase!
When we were first approached with this improved fish oil extraction technology, the first thing we said is “no higher prices.” Consumers today are already taking a lot of supplements and most cannot afford higher prices for staples such as fish oil.
The good news is that despite the costly processes involved in making this new fish oil extract, the price of our Super Omega-3 remains the same!
Life Extension members thus gain access to a superior fish oil extract at no additional cost.
Does the improved purity really matter?
 The fish oil used previously in Super Omega-3 always tested out below the allowable limits for pollutants and received the coveted 5-star rating from the International Fish Oil Society. So does removing even more contaminants really matter?
The fish oil used previously in Super Omega-3 always tested out below the allowable limits for pollutants and received the coveted 5-star rating from the International Fish Oil Society. So does removing even more contaminants really matter?
The answer is that no one knows for sure. What we do recognize is that mercury is toxic to cells throughout the body and that PCBs are potent carcinogens. It makes common sense to want to ingest fewer pollutants. A recent study from Cornell University estimated that one-third of worldwide deaths are caused by pollution.1
Our view of standards set for acceptable levels of pollutants is that they are based on typical life spans. Since Foundation members expect to greatly exceed “average” longevities, reducing one’s exposure to pollutants would appear desirable. It is also important to point out that pollutants are ubiquitous in our environment, and the best we can ever do is reduce our exposure levels. (Cruciferous vegetables and/or supplements like indole-3-carbinol and chlorophyllin help protect our cells against environmental pollutants.)
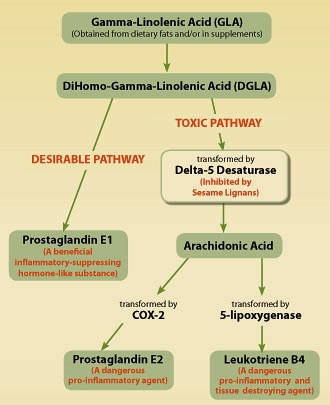
Chart 1: This chart shows that GLA can follow a pro-inflammatory or anti-inflammatory pathway in the body. Sesame lignans suppress the enzyme (delta-5 desaturase) that converts DGLA into arachidonic acid. By blocking the undesirable enzyme (delta-5 desaturase), more DGLA is available for conversion into beneficial prostaglandin E1.5-10
What makes Super Omega-3 the best fish oil supplement?
 Consumers have access to a wide range of omega-3 supplements. The overwhelming preponderance of evidence indicates that obtaining EPA and DHA directly from fish oil is the most effective way of benefiting from these essential fatty acids.
Consumers have access to a wide range of omega-3 supplements. The overwhelming preponderance of evidence indicates that obtaining EPA and DHA directly from fish oil is the most effective way of benefiting from these essential fatty acids.
Life Extension’s Super Omega-3 is the only fish concentrate that provides a full spectrum blend of fatty acids and synergistic nutrients to provide optimal effects in the body.
Three years ago, Life Extension uncovered research showing that the addition of sesame lignans to fish oil enhances its beneficial effects.2 When fats are consumed, they are broken down into compounds that either promote or suppress inflammatory reactions. Specialized enzymes in the body determine which inflammatory pathway fats will follow.
Sesame lignans inhibit an enzyme (delta-5 desaturase) that causes DGLA (dihomo-gamma-linolenic acid) to be converted into arachidonic acid, a precursor to the toxic inflammatory factors prostaglandin E2 and the leukotrienes.3
Sesame lignans also increase levels of DGLA (dihomo-gamma-linolenic acid), the precursor to prostaglandin E1. Prostaglandin E1 has demonstrated health benefits including blood vessel relaxation and suppression of inflammation.4 (Chart 1 shows how sesame can influence delta-5 desaturase, and the subsequent path down which dietary fats cascade.)
GLA (gamma-linolenic acid) is a dietary fat that can increase levels of DGLA and beneficial prostaglandin E1 in the body. When sesame lignans are combined with fish oil, DGLA levels rise dramatically and the anti-inflammatory benefit of the fish oil greatly improves.
For consumers, this means that taking fish oil with sesame lignans may provide comparable benefits to fish and borage oil (GLA) supplements. Super Omega-3 contains a standardized sesame lignan extract to provide users with these synergistic benefits shown in scientific studies.
Extending the stability of fish oil in the body
 Whenever a polyunsaturated fat like fish oil is consumed, it may degrade into byproducts that have no value and even generate excess free-radical activity. Sesame functions as a powerful antioxidant, and its addition to fish oil lowers undesirable lipid peroxidation rates.11,12
Whenever a polyunsaturated fat like fish oil is consumed, it may degrade into byproducts that have no value and even generate excess free-radical activity. Sesame functions as a powerful antioxidant, and its addition to fish oil lowers undesirable lipid peroxidation rates.11,12
Sesame suppresses the formation of free radicals from the DHA fraction of fish oil, which has extremely high oxidative susceptibility.14 A test of this effect was confirmed in rats fed a high DHA diet from fish oil. In the first part of the study, DHA alone lowered vitamin E levels and raised a measure of free radical damage. The addition of sesame raised plasma and liver vitamin E levels higher, increased concentrations of DHA, and completely suppressed free radical production from the DHA in tissues and serum.11
The combination of sesame and fish oil (as found in the Super Omega-3 formula) thus helps to suppress free radical production of fish oil by blocking lipid peroxidation and simultaneously boosting levels of beneficial fatty acids (such as DGLA and DHA).11,13
Increased burning of blood lipids
 In order for cells to produce energy, they must burn fatty acids in their mitochondria. The failure of liver mitochondria to properly burn fatty acids can result in excess accumulation of triglycerides.
In order for cells to produce energy, they must burn fatty acids in their mitochondria. The failure of liver mitochondria to properly burn fatty acids can result in excess accumulation of triglycerides.
Triglycerides not burned in the liver accumulate in the blood and contribute to arterial occlusion.
When rats were fed sesame lignans and fish oil together, their hepatic fatty acid oxidation rates rose much higher than when fed fish oil alone. This study pointed out that the sesame-fish oil combination worked synergistically by increasing the fatty acid oxidation enzymes in the liver.10
Thus, the combination of fish oil with sesame improves mitochondrial fatty acid energy utilization, which facilitates triglyceride reduction, while also guarding against the free radicals generated as an inevitable consequence of higher cellular metabolism.11,15,16
Virtues of the Mediterranean diet
 A large body of human data indicates potent health benefits in those who consume a Mediterranean diet, characterized by relatively copious amounts of fish, olive oil, fruits, vegetables, and herbs.
A large body of human data indicates potent health benefits in those who consume a Mediterranean diet, characterized by relatively copious amounts of fish, olive oil, fruits, vegetables, and herbs.
The predominant fats in the Mediterranean diet are the omega-3s and monounsaturated fats from olive oil. While the monounsaturated fats in olive oil are a crucial component of the Mediterranean diet, the rich mixture of polyphenols in the olive fruit appears to be equally important.17
For example, published studies have shown that the olive fruit polyphenol—hydroxytyrosol—scavenges the dangerous free radical hydrogen peroxide and reduces LDL susceptibility to oxidation.18 The oxidation of LDL plays a significant role in the development of vascular impairment.
In a randomized, double-blind, crossover study, human subjects consumed three different extra-virgin olive oils with incrementally greater levels of polyphenols. The results showed that as the polyphenol content of the olive oil increased, the oxidation of LDL decreased. Polyphenol-rich olive oil also raised beneficial HDL levels. Both effects are associated with an improved cardiovascular risk profile.19
In another study, researchers tested the effects of feeding three olive oils with incrementally greater levels of polyphenols to a group of healthy male volunteers. Subjects in this randomized, double-blind study consumed standardized doses of polyphenol-rich olive oil. The results showed that oxidized LDL decreased, glutathione antioxidant activity increased, and beneficial HDL levels increased in the participants. These effects were proportionally greater as olive polyphenol content increased. All of these changes reflect improvements in surrogate markers of cardiovascular health.20
Super Omega-3 contains a standardized olive fruit extract to provide the full spectrum of benefits associated with the ingestion of fish and olive oils, including the potent hydroxytyrosol polyphenol.
One reason people supplement with fish oil is to suppress the production of arachidonic acid in the body. To better understand how arachidonic acid can cause arthritic and cardiovascular conditions, the chart below shows how arachidonic acid cascades down into joint-destroying, pro-thrombotic compounds.
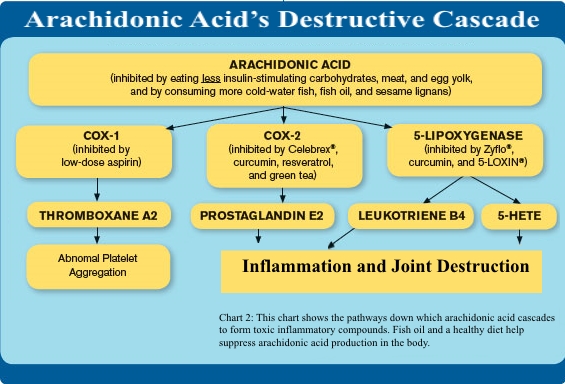
Chart 2: This chart shows the pathways down which arachidonic acid cascades to form toxic inflammatory compounds. Fish oil and a healthy diet help suppress arachidonic acid production in the body.
New olive oil extract
 When investigating why consumption of olive foods results in such marked reductions in human maladies, scientists uncovered another olive polyphenol that functions via specific beneficial mechanisms.
When investigating why consumption of olive foods results in such marked reductions in human maladies, scientists uncovered another olive polyphenol that functions via specific beneficial mechanisms.
Blood platelets guard against excessive bleeding. When our platelets become over-activated, they can form clots inside arteries leading to acute circulatory disruptions. An olive fruit polyphenol called oleuropein has been shown to specifically reduce blood platelet activity in humans,21 thus providing yet another explanation as to why those who consume a Mediterranean diet have such low rates of sudden vascular events.
Oleuropein from olive fruit has additional biological properties. When administered to human fibroblast skin cells cultures, oleuropein delays the appearance of senescent (aging) structural changes and increases the life span of these cells by approximately 15%.22 The scientists who conducted this study stated: “these data demonstrate the beneficial effect of oleuropein on human fibroblasts undergoing replicative senescence and provide new insights toward enhancement of cellular antioxidant mechanisms by natural compounds that can be easily up-taken through normal diet.”
Those afflicted with certain inherited genetic mutations are predisposed to contracting disorders related to defects in cell replication. A gene of particular concern to some women is HER2. When evaluating various olive polyphenols on HER2 expression, oleuropein most effectively down-regulated HER2 expression.23 The scientists who conducted this study remarked that their findings help explain why those who consume a Mediterranean diet have such marked reductions in disorders related to excess expression of the HER2 gene.
Super Omega-3 not only contains the finest omega-3 fish oil blend in the world, but also provides an olive blend standardized for hydroxytyrosol and oleuropein.
Olive oil and fish oil work better together than fish oil alone
 Patients suffering from chronic age-related discomforts were randomized into three groups. The first group received EPA/DHA-rich fish oil, the second group received the same fish oil with polyphenol-rich olive oil, while the third group received a placebo.
Patients suffering from chronic age-related discomforts were randomized into three groups. The first group received EPA/DHA-rich fish oil, the second group received the same fish oil with polyphenol-rich olive oil, while the third group received a placebo.
At the study’s end, the fish oil-only group showed significant improvement in several measurements. The group receiving both fish oil and polyphenol-enriched olive oil, however, exhibited an “accentuated improvement” across a broad-spectrum of parameters including patients’ subjective assessments and satisfaction with their daily living activities.24
This study helps further corroborate the multiple health benefits associated with the Mediterranean diet, rich in monounsaturated and omega-3 fatty acids, along with plant polyphenols.
The new Super Omega-3…even better quality…same low price! No drug has ever shown the broad-spectrum health benefits of fish oil.
Each year, consumers pay higher prices for patented medications that have only limited therapeutic targets. These drugs are also known to induce side effects, despite the FDA’s assurance of their safety.
Life Extension’s new Super Omega-3 provides the purest EPA/DHA fish oil blend, standardized sesame lignans, and the most beneficial extracts from the olive fruit at no additional charge.
If the government ever turned dietary supplements into prescription drugs, it would not be possible to make these rapid improvements, as the FDA would mandate a new round of costly clinical testing every time a change was made. The end result might be an improved (and higher priced) drug many years down the road, depending on the FDA bureaucratic decision-making process.
Life Extension has a dual mission of providing members with the finest nutritional formulations while leading by example in showing the superiority of the free market over today’s regulatory quagmire that strangles medical innovation.
Material used with permission of Life Extension. All rights reserved.
1. David Pimentel, et al. Ecology of Increasing Disease. BioScience, Vol. 48, No. 10 (Oct., 1998), pp. 817-826
2. Ide, T, Hong, DD, Ranasinghe, P, et al. Interaction of dietary fat types and sesamin on hepatic fatty acid oxidation in rats. Biochem Biophys Acta. 2004 Jun 1;1682(1-3):80-91.
3. Utsunomiya, T, Chavali, SR, Zhong, WW, et al. Effects of sesamin-supplemented dietary fat emulsions on the production of lipopolysaccharide-induced prostanoids and tumor necrosis factor alpha in rats. Am J Clin Nutr. 2000 Sep;72(3):804-8.
4. Chavali, SR, Zhong, WW, Forse, RA Dietary alpha-linolenic acid increases TNF-alpha, and decreases IL-6, IL-10 in response to LPS: effects of delta-5-desaturation of omega6 and omega3 fatty acids in mice. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 1998 Mar;58(3):185-91.
5. Umeda-Sawada R, Ogawa M, Igarashi O. The metabolism and N-6/N-3 ratio of essential fatty acids in rats: effect of dietary arachidonic acid and a mixture of sesame lignans (sesamin and episesamin). Lipids. 1998 Jun;33(6):567-72.
6. Shimizu S, Akimoto K, Shinmen Y, et al. Sesamin is a potent and specific inhibitor of delta-5-desaturase in polyunsaturated fatty acid biosynthesis. Lipids. 1991 Jul;26(7):512-6.
7. Fujiyama-Fujiwara Y, Umeda-Sawada R, Kuzuyama M, Igarashi O. Effects of sesamin on the fatty acid composition of the liver of rats fed N-6 and N-3 fatty acid rich diet. J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. (Tokyo) 1995 Apr;41(2):217-25.
8. Gu JY, Wakizono Y, Tsujita A, et al. Effects of sesamin and alpha-tocopherol, individually or in combination, on the polyunsaturated fatty-acid metabolism, chemical mediator production, and immunoglobulin levels in Sprague-Dawley rats. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 1995 Dec; 59(12):2198-202.
9. Chavali SR, Zhong WW, Forse RA. Dietary alpha-linolenic acid increases TNF-alpha, and decreases IL-6, IL-10 in response to LPS: effects of sesamin on the delta-5 desaturation of omega6 and omega3 fatty acids in mice. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 1998 Mar;58(3):185-91.
10. Akimoto K, Kitagawa Y, Akamatsu T, et al. Protective effects of sesamin against liver damage caused by alcohol or carbon tetrachloride in rodents. Ann Nutr Metab. 1993;37(4):218-24.
11. Ikeda S, Kagaya M, Kobayashi K, et al. Dietary sesame lignans decrease lipid peroxidation in rats fed docosahexaenoic acid. J Nutr Sci Vitaminol. (Tokyo). 2003 Aug;49(4):270-6.
12. Kang M, Katsuzaki H, Osawa T. Inhibition of 2,2’-azobis[2,4-dimethylvaleronitrile]-induced lipid peroxidation by sesaminols. Lipids. 1998;33(10):1031-6.
13. Chavali SR, Zhong WW, Forse RA. Dietary alpha-linolenic acid increases TNF-alpha, and decreases IL-6, IL-10 in response to LPS: effects of delta-5-desaturation of omega6 and omega3 fatty acids in mice. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 1998 Mar;58(3):185-91.
14. Yamashita K, Kagaya M, Higuti N, et al. Sesamin and alpha-tocopherol synergistically suppress lipid-peroxide in rats fed a high docosahexaenoic acid diet. Biofactors. 2000;11(1-2):11-3.
15. Ashakumary L, Rouyer I, Takahashi Y, et al. Sesamin, a sesame lignan is a potent inducer of hepatic fatty acid oxidation in the rat. Metabolism. 1999 Oct;48(10):1303-13.
16. Kushiro M, Masaoka T, Hageshita S, et al. Comparative effect of sesamin and episesamin on the activity and gene expression of enzymes in fatty acid oxidation and synthesis in rat liver. J Nutr Biochem. 2002 May;13(5):289-295.
17. Trichopoulou A, Vasilopoulou E. Mediterranean diet and longevity. Br J Nutr. 2000 Dec;84 Suppl 2:S205-9.
18. Rietjens SJ, Bast A, Haenen GR. New insights into controversies on the antioxidant potential of the olive oil antioxidant hydroxytyrosol. J Agric Food Chem. 2007 Sep 5;55(18):7609-14.
19. Weinbrenner T, Fito M, de la Torre R, et al. Olive oils high in phenolic compounds modulate oxidative/antioxidative status in men. J Nutr. 2004 Sep;134(9):2314-21.
20. Gimeno E, Fito M, Lamuela-Raventos RM, et al. Effect of ingestion of virgin olive oil on human low-density lipoprotein composition. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2002 Feb;56(2):114-20.
21. Singh I, Mok M, Christensen AM, Turner AH, Hawley JA. The effects of polyphenols in olive leaves on platelet function. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2007 Mar 6.
22. Katsiki M, Chondrogianni N, Chinou I, Rivett AJ, Gonos ES. The olive constituent oleuropein exhibits proteasome stimulatory properties in vitro and confers life span extension of human embryonic fibroblasts. Rejuvenation Res. 2007 Jun;10(2):157-72.
23. Menendez JA, Vazquez-Martin A, Colomer R, Brunet J, Carrasco-Pancorbo A, Garcia-Villalba R, Fernandez-Gutierrez A, Segura-Carretero A. Olive oil’s bitter principle reverses acquired autoresistance to trastuzumab (Herceptin) in HER2-overexpressing breast cancer cells. BMC Cancer. 2007 May 9;7:80.
24. Berbert AA, Kondo CR, Alemendra CL, Matsuo T, Dichi I. Supplementation of fish oil and olive oil in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Nutrition. 2005 Feb;21(2):131-6.






